前言
大家好,这里是RT-DETR有效涨点专栏。
本专栏的内容为根据ultralytics版本的RT-DETR进行改进,内容持续更新,每周更新文章数量3-10篇。
专栏以ResNet18、ResNet50为基础修改版本,同时修改内容也支持ResNet32、ResNet101和PPHGNet版本,其中ResNet为RT-DETR官方版本1:1移植过来的,参数量基本保持一致(误差很小很小),不同于ultralytics仓库版本的ResNet官方版本,同时ultralytics仓库的一些参数是和RT-DETR相冲的所以我也是会教大家调好一些参数和代码,真正意义上的跑ultralytics的和RT-DETR官方版本的无区别。
👑欢迎大家订阅本专栏,一起学习RT-DETR👑
一、本文介绍
本文给大家带来的改进机制是MobileNetV3,其主要改进思想集中在结合硬件感知的网络架构搜索(NAS)和NetAdapt算法,以优化移动设备CPU上的性能。它采用了新颖的架构设计,包括反转残差结构和线性瓶颈层,以及新的高效分割解码器Lite Reduced Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling(LR-ASPP),以提升在移动分类、检测和分割任务上的表现。实验表明,MobileNets在资源和准确性的权衡方面表现出色,并在多种应用(如对象检测、细粒度分类、面部属性识别和大规模地理定位)中展现了其有效性,可以看出其mAP增加了大概三四个点,同时参数量却下降了百分之四十以上!
专栏链接:RT-DETR剑指论文专栏,持续复现各种顶会内容——论文收割机RT-DETR
目录
一、本文介绍
二、MobileNetV3的框架原理
2.1 NAS和NetAdapt算法
2.2 反转残差结构和线性瓶颈层
三、MobileNetV3的核心代码
四、手把手教你添加MobileNetV3网络结构
4.1 修改一
4.2 修改二
4.3 修改三
4.4 修改四
4.5 修改五
4.6 修改六
4.7 修改七
4.8 修改八
4.9 RT-DETR不能打印计算量问题的解决
4.10 可选修改
五、MobileNetV3的yaml文件
5.1 yaml文件
5.2 运行文件
5.3 成功训练截图
六、全文总结
二、MobileNetV3的框架原理

官方论文地址:官方论文地址点击即可跳转
官方代码地址:官方代码地址
MobileNetV3的主要改进思想集中在结合硬件感知的网络架构搜索(NAS)和NetAdapt算法,以优化移动设备CPU上的性能。它采用了新颖的架构设计,包括反转残差结构和线性瓶颈层,以及新的高效分割解码器Lite Reduced Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling(LR-ASPP),以提升在移动分类、检测和分割任务上的表现。这些改进通过精心设计的轻量级架构,实现了更高的准确度、更低的延迟,并在不同的资源使用场景中实现了更好的性能。
MobileNetV3的主要创新点包括:
1. 结合了硬件感知的网络架构搜索(NAS)和NetAdapt算法,针对移动设备CPU进行优化。
2. 引入了新颖的架构设计,包括反转残差结构和线性瓶颈层。
3. 提出了高效的Lite Reduced Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling(LR-ASPP)作为新的分割解码器。
2.1 NAS和NetAdapt算法
MobileNetV3采用了硬件感知的网络架构搜索(NAS)和NetAdapt算法,这两种技术相互补充,可以结合起来有效地为特定硬件平台找到优化的模型。特别是,它采用了平台感知NAS进行块级搜索,类似于之前的MnasNet-A1方法,使用相同的基于RNN的控制器和相同的分解层次搜索空间,以便为大型移动模型找到全局网络结构,目标是大约80ms的延迟。然后在此基础上应用NetAdapt算法和其他优化措施。这种方法允许在顺序方式中对单个层进行微调,而不是尝试推断粗略但全局的架构。NetAdapt的第二个技术是用于层级搜索,它更适用于小型移动模型,因为对于小型模型来说,准确性随着延迟的变化更加显著,因此需要一个较小的权重因子w = -0.15来补偿不同延迟下的较大准确性变化。通过这个新的权重因子,我们从头开始一个新的架构搜索,以找到初始种子模型,然后应用NetAdapt和其他优化来获得最终的MobileNetV3-Small模型
2.2 反转残差结构和线性瓶颈层
MobileNetV3在架构上进行了一些修改,以降低某些较慢层的延迟,同时保持准确性。这些修改超出了当前搜索空间的范围。第一项修改重新设计了网络的最后几层是如何相互作用以更有效地生成最终特征的。基于MobileNetV2的反转瓶颈结构的当前模型在最终层使用1x1卷积以扩展到更高维的特征空间。这一层对于预测中拥有丰富的特征至关重要。然而,这也增加了额外的延迟。为了减少延迟并保留高维特征,我们将这一层移到最终的平均池化之后

上图展示了MobileNetV2和MobileNetV3的网络结构层。
上侧 (MobileNetV2层):展示了反转残差和线性瓶颈结构。每个块由狭窄的输入和输出层组成,这些层没有非线性操作,后面跟着扩展到更高维空间并投影到输出的操作。残差连接连接了瓶颈层,而不是扩展层。
下侧 (MobileNetV2 + Squeeze-and-Excite): 展示了与Squeeze-and-Excite层一起使用的MobileNetV3。与先前不同,在残差层中应用了挤压和激励操作。
三、MobileNetV3的核心代码
下面的代码是整个MobileNetV1的核心代码,大家如果想学习可以和上面的框架原理对比着看一看估计会有一定的收获,使用方式看章节四。
"""A from-scratch implementation of MobileNetV3 paper ( for educational purposes ).
Paper
Searching for MobileNetV3 - https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244v5
author : shubham.aiengineer@gmail.com
"""
import torch
from torch import nn
from torchsummary import summary
class SqueezeExitationBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels: int):
"""Constructor for SqueezeExitationBlock.
Args:
in_channels (int): Number of input channels.
"""
super().__init__()
self.pool1 = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(
in_channels, in_channels // 4
) # divide by 4 is mentioned in the paper, 5.3. Large squeeze-and-excite
self.act1 = nn.ReLU()
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(in_channels // 4, in_channels)
self.act2 = nn.Hardsigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward pass for SqueezeExitationBlock."""
identity = x
x = self.pool1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
x = self.act2(x)
x = identity * x[:, :, None, None]
return x
class ConvNormActivationBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size: list,
stride: int = 1,
padding: int = 0,
groups: int = 1,
bias: bool = False,
activation: torch.nn = nn.Hardswish,
):
"""Constructs a block containing a convolution, batch normalization and activation layer
Args:
in_channels (int): number of input channels
out_channels (int): number of output channels
kernel_size (list): size of the convolutional kernel
stride (int, optional): stride of the convolutional kernel. Defaults to 1.
padding (int, optional): padding of the convolutional kernel. Defaults to 0.
groups (int, optional): number of groups for depthwise seperable convolution. Defaults to 1.
bias (bool, optional): whether to use bias. Defaults to False.
activation (torch.nn, optional): activation function. Defaults to nn.Hardswish.
"""
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
bias=bias,
)
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.activation = activation()
def forward(self, x):
"""Perform forward pass."""
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
class InverseResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size: int,
expansion_size: int = 6,
stride: int = 1,
squeeze_exitation: bool = True,
activation: nn.Module = nn.Hardswish,
):
"""Constructs a inverse residual block
Args:
in_channels (int): number of input channels
out_channels (int): number of output channels
kernel_size (int): size of the convolutional kernel
expansion_size (int, optional): size of the expansion factor. Defaults to 6.
stride (int, optional): stride of the convolutional kernel. Defaults to 1.
squeeze_exitation (bool, optional): whether to add squeeze and exitation block or not. Defaults to True.
activation (nn.Module, optional): activation function. Defaults to nn.Hardswish.
"""
super().__init__()
self.residual = in_channels == out_channels and stride == 1
self.squeeze_exitation = squeeze_exitation
self.conv1 = (
ConvNormActivationBlock(
in_channels, expansion_size, (1, 1), activation=activation
)
if in_channels != expansion_size
else nn.Identity()
) # If it's not the first layer, then we need to add a 1x1 convolutional layer to expand the number of channels
self.depthwise_conv = ConvNormActivationBlock(
expansion_size,
expansion_size,
(kernel_size, kernel_size),
stride=stride,
padding=kernel_size // 2,
groups=expansion_size,
activation=activation,
)
if self.squeeze_exitation:
self.se = SqueezeExitationBlock(expansion_size)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(
expansion_size, out_channels, (1, 1), bias=False
) # bias is false because we are using batch normalization, which already has bias
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
"""Perform forward pass."""
identity = x
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.depthwise_conv(x)
if self.squeeze_exitation:
x = self.se(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.norm(x)
if self.residual:
x = x + identity
return x
class MobileNetV3(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
n_classes: int = 1000,
input_channel: int = 3,
config: str = "large",
dropout: float = 0.8,
):
"""Constructs MobileNetV3 architecture
Args:
`n_classes`: An integer count of output neuron in last layer, default 1000
`input_channel`: An integer value input channels in first conv layer, default is 3.
`config`: A string value indicating the configuration of MobileNetV3, either `large` or `small`, default is `large`.
`dropout` [0, 1] : A float parameter for dropout in last layer, between 0 and 1, default is 0.8.
"""
super().__init__()
# The configuration of MobileNetv3.
# input channels, kernel size, expension size, output channels, squeeze exitation, activation, stride
RE = nn.ReLU
HS = nn.Hardswish
configs_dict = {
"small": (
(16, 3, 16, 16, True, RE, 2),
(16, 3, 72, 24, False, RE, 2),
(24, 3, 88, 24, False, RE, 1),
(24, 5, 96, 40, True, HS, 2),
(40, 5, 240, 40, True, HS, 1),
(40, 5, 240, 40, True, HS, 1),
(40, 5, 120, 48, True, HS, 1),
(48, 5, 144, 48, True, HS, 1),
(48, 5, 288, 96, True, HS, 2),
(96, 5, 576, 96, True, HS, 1),
(96, 5, 576, 96, True, HS, 1),
),
"large": (
(16, 3, 16, 16, False, RE, 1),
(16, 3, 64, 24, False, RE, 2),
(24, 3, 72, 24, False, RE, 1),
(24, 5, 72, 40, True, RE, 2),
(40, 5, 120, 40, True, RE, 1),
(40, 5, 120, 40, True, RE, 1),
(40, 3, 240, 80, False, HS, 2),
(80, 3, 200, 80, False, HS, 1),
(80, 3, 184, 80, False, HS, 1),
(80, 3, 184, 80, False, HS, 1),
(80, 3, 480, 112, True, HS, 1),
(112, 3, 672, 112, True, HS, 1),
(112, 5, 672, 160, True, HS, 2),
(160, 5, 960, 160, True, HS, 1),
(160, 5, 960, 160, True, HS, 1),
),
}
self.model = nn.Sequential(
ConvNormActivationBlock(
input_channel, 16, (3, 3), stride=2, padding=1, activation=nn.Hardswish
),
)
for (
in_channels,
kernel_size,
expansion_size,
out_channels,
squeeze_exitation,
activation,
stride,
) in configs_dict[config]:
self.model.append(
InverseResidualBlock(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
expansion_size=expansion_size,
stride=stride,
squeeze_exitation=squeeze_exitation,
activation=activation,
)
)
hidden_channels = 576 if config == "small" else 960
_out_channel = 1024 if config == "small" else 1280
self.model.append(
ConvNormActivationBlock(
out_channels,
hidden_channels,
(1, 1),
bias=False,
activation=nn.Hardswish,
)
)
self.index = [16, 24, 48, 576]
self.width_list = [i.size(1) for i in self.forward(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))]
def forward(self, x):
"""Perform forward pass."""
results = [None, None, None, None]
for model in self.model:
x = model(x)
if x.size(1) in self.index:
position = self.index.index(x.size(1)) # Find the position in the index list
results[position] = x
return results
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Generating Sample image
image_size = (1, 3, 224, 224)
image = torch.rand(*image_size)
# Model
mobilenet_v3 = MobileNetV3(config="small")
# summary(
# mobilenet_v3,
# input_data=image,
# col_names=["input_size", "output_size", "num_params"],
# device="cpu",
# depth=2,
# )
out = mobilenet_v3(image)
print("Output shape : ", out.shape)四、手把手教你添加MobileNetV3网络结构
下面教大家如何修改该网络结构,主干网络结构的修改步骤比较复杂,我也会将task.py文件上传到CSDN的文件中,大家如果自己修改不正确,可以尝试用我的task.py文件替换你的,然后只需要修改其中的第1、2、3、5步即可。
⭐修改过程中大家一定要仔细⭐
4.1 修改一
首先我门中到如下“ultralytics/nn”的目录,我们在这个目录下在创建一个新的目录,名字为'Addmodules'(此文件之后就用于存放我们的所有改进机制),之后我们在创建的目录内创建一个新的py文件复制粘贴进去 ,可以根据文章改进机制来起,这里大家根据自己的习惯命名即可。
4.2 修改二
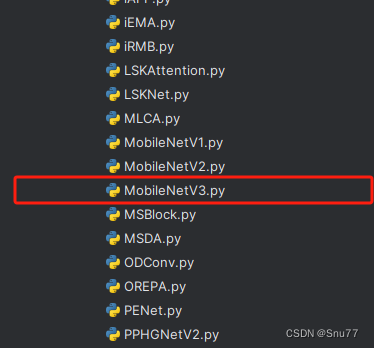
第二步我们在我们创建的目录内创建一个新的py文件名字为'__init__.py'(只需要创建一个即可),然后在其内部导入我们本文的改进机制即可。
4.3 修改三
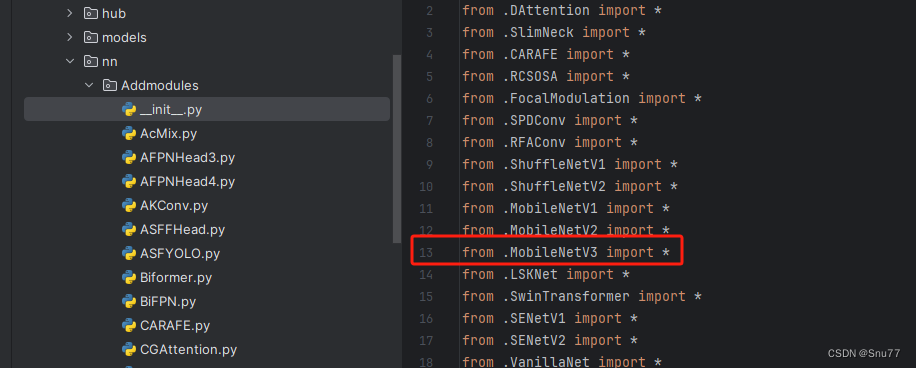
第三步我门中到如下文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'然后在开头导入我们的所有改进机制(如果你用了我多个改进机制,这一步只需要修改一次即可)。
4.4 修改四
添加如下两行代码!!!

4.5 修改五
找到七百多行大概把具体看图片,按照图片来修改就行,添加红框内的部分,注意没有()只是函数名。

elif m in {自行添加对应的模型即可,下面都是一样的}:
m = m(*args)
c2 = m.width_list # 返回通道列表
backbone = True4.6 修改六
用下面的代码替换红框内的内容。
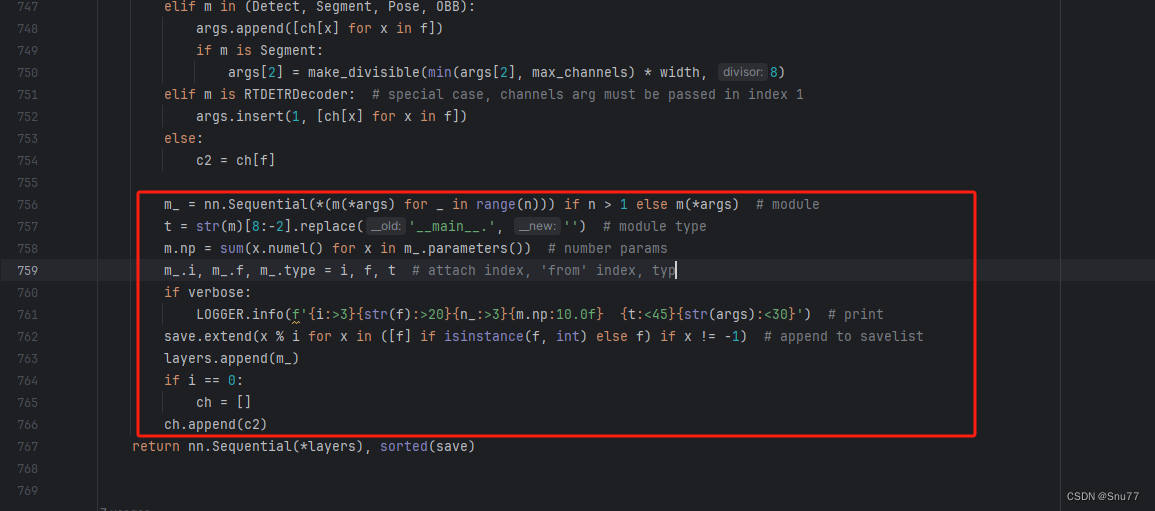
if isinstance(c2, list):
m_ = m
m_.backbone = True
else:
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i + 4 if backbone else i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(
x % (i + 4 if backbone else i) for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
if isinstance(c2, list):
ch.extend(c2)
if len(c2) != 5:
ch.insert(0, 0)
else:
ch.append(c2)4.7 修改七
修改七我们需要来到文件的开头,然后将下面红框内的部分用我给的代码进行替换即可,同时大家主意好不要替换错了!!
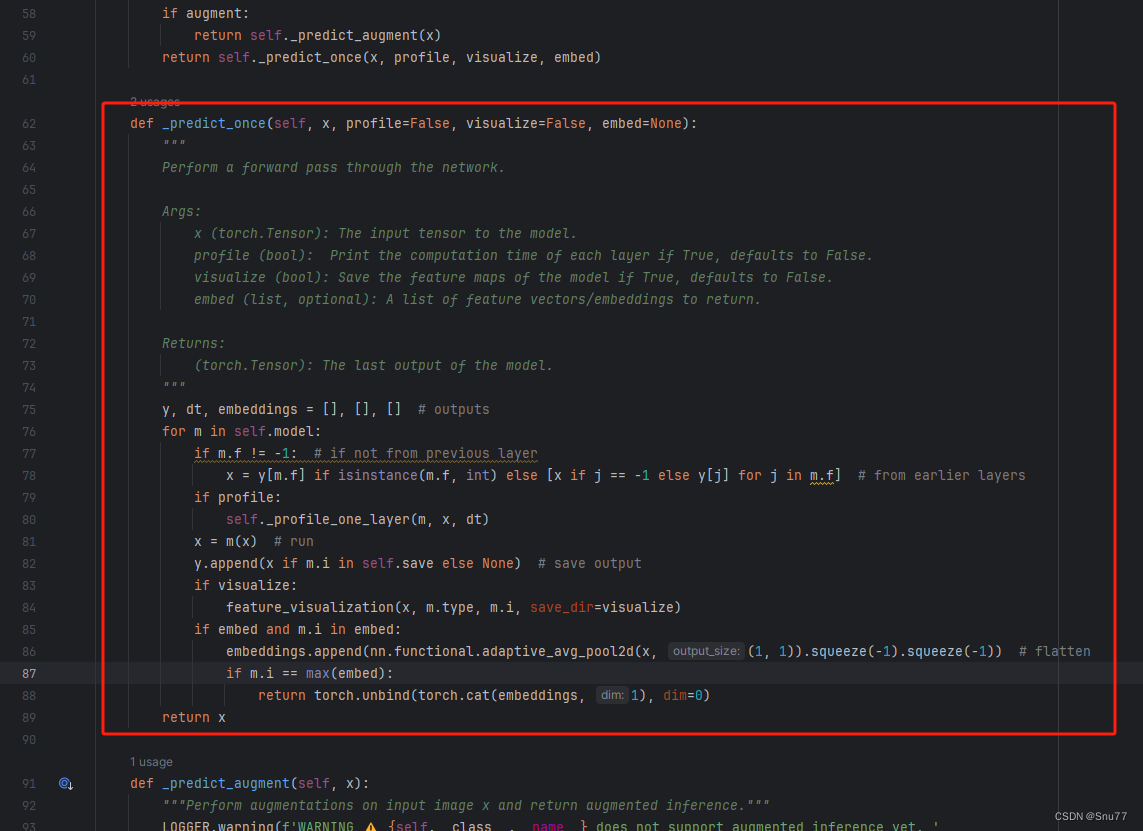
代码如下->
def _predict_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
y, dt = [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
if hasattr(m, 'backbone'):
x = m(x)
if len(x) != 5: # 0 - 5
x.insert(0, None)
for index, i in enumerate(x):
if index in self.save:
y.append(i)
else:
y.append(None)
x = x[-1] # 最后一个输出传给下一层
else:
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
return x到这里就完成了修改部分,但是这里面细节很多,大家千万要注意不要替换多余的代码,导致报错,也不要拉下任何一部,都会导致运行失败,而且报错很难排查!!!很难排查!!!
4.8 修改八
我们将下面的s用640替换即可,这一步也是部分的主干可以不修改,但有的不修改就会报错,所以我们还是修改一下。
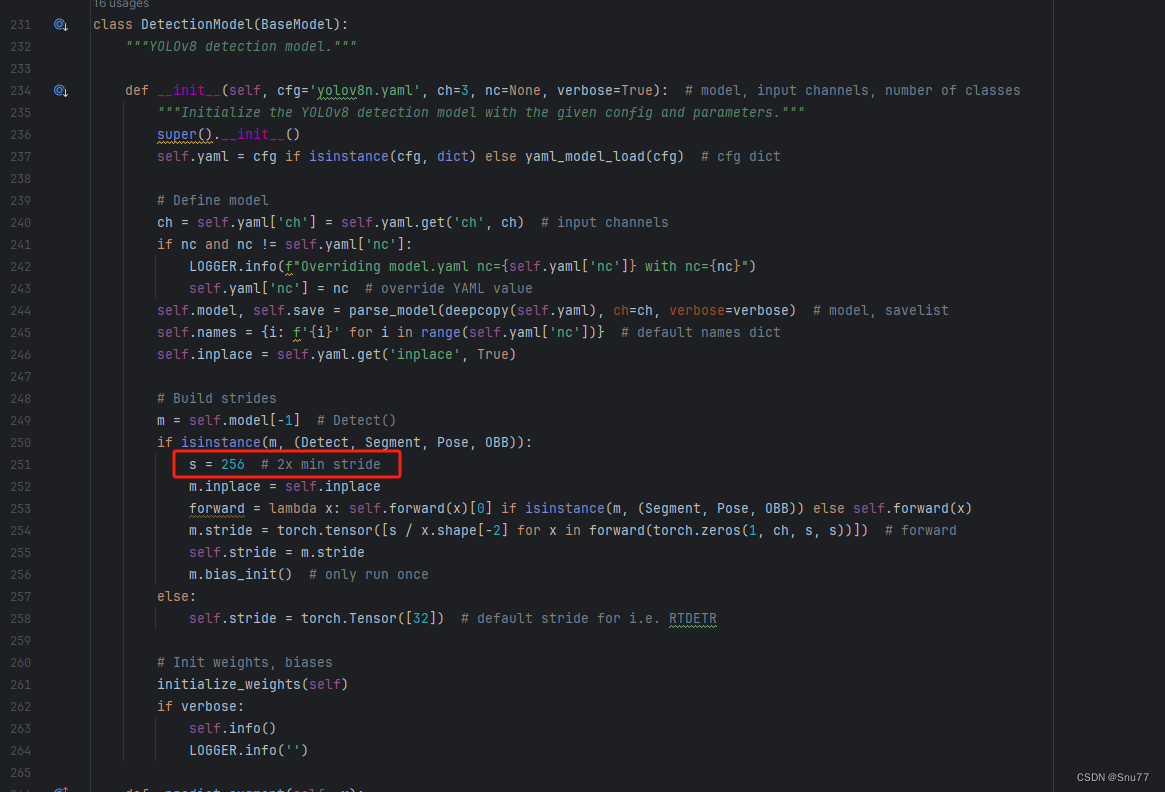
4.9 RT-DETR不能打印计算量问题的解决
我们找到如下文件'ultralytics/utils/torch_utils.py'按照如下的图片进行修改,来解决计算量打印不出来的问题。
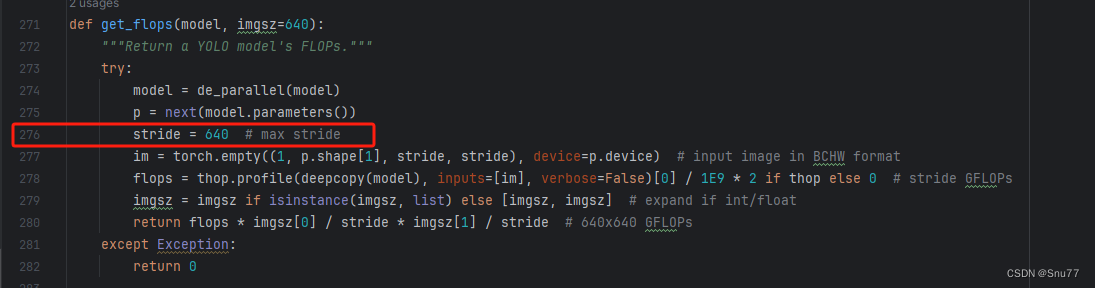
4.10 可选修改
有些读者的数据集部分图片比较特殊,在验证的时候会导致形状不匹配的报错,如果大家在验证的时候报错形状不匹配的错误可以固定验证集的图片尺寸,方法如下 ->
找到下面这个文件ultralytics/models/yolo/detect/train.py然后其中有一个类是DetectionTrainer class中的build_dataset函数中的一个参数rect=mode == 'val'改为rect=False

五、MobileNetV3的yaml文件
5.1 yaml文件
大家复制下面的yaml文件,然后通过我给大家的运行代码运行即可,RT-DETR的调参部分需要后面的文章给大家讲,现在目前免费给大家看这一部分不开放。
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# RT-DETR-l object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For details see https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/rtdetr
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n-cls.yaml' will call yolov8-cls.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
l: [1.00, 1.00, 1024]
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, MobileNetV3, []] # 4
head:
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 5 input_proj.2
- [-1, 1, AIFI, [1024, 8]] # 6
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]] # 7, Y5, lateral_convs.0
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] # 8
- [3, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 9 input_proj.1
- [[-2, -1], 1, Concat, [1]] # 10
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # 11, fpn_blocks.0
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]] # 12, Y4, lateral_convs.1
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] # 13
- [2, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 14 input_proj.0
- [[-2, -1], 1, Concat, [1]] # 15 cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # X3 (16), fpn_blocks.1
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 17, downsample_convs.0
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # 18 cat Y4
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # F4 (19), pan_blocks.0
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 20, downsample_convs.1
- [[-1, 7], 1, Concat, [1]] # 21 cat Y5
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # F5 (22), pan_blocks.1
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, RTDETRDecoder, [nc, 256, 300, 4, 8, 3]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
5.2 运行文件
大家可以创建一个train.py文件将下面的代码粘贴进去然后替换你的文件运行即可开始训练。
import warnings
from ultralytics import RTDETR
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = RTDETR('替换你想要运行的yaml文件')
# model.load('') # 可以加载你的版本预训练权重
model.train(data=r'替换你的数据集地址即可',
cache=False,
imgsz=640,
epochs=72,
batch=4,
workers=0,
device='0',
project='runs/RT-DETR-train',
name='exp',
# amp=True
)5.3 成功训练截图
下面是成功运行的截图(确保我的改进机制是可用的),已经完成了有1个epochs的训练,图片太大截不全第2个epochs了。
六、全文总结
从今天开始正式开始更新RT-DETR剑指论文专栏,本专栏的内容会迅速铺开,在短期呢大量更新,价格也会乘阶梯性上涨,所以想要和我一起学习RT-DETR改进,可以在前期直接关注,本文专栏旨在打造全网最好的RT-DETR专栏为想要发论文的家进行服务。
专栏链接:RT-DETR剑指论文专栏,持续复现各种顶会内容——论文收割机RT-DETR